- Go to sqlservr.exe in the task manager processes
- Terminate the process
- Go to Services
- Start SQL Server(SQL Express)
- Try to connect again
Showing posts with label SQL Server. Show all posts
Showing posts with label SQL Server. Show all posts
Monday, April 15, 2013
A network-related or instance-specific error occurred while establishing a connection to SQL Server. The server was not found or was not accessible. Verify that the instance name is correct and that SQL Server is configured to allow remote connections.
Try following! It worked for me. :)
Wednesday, February 15, 2012
Multi-dimensional databases vs Relational databases
Just back from the SQL Server user group meeting and the first topic was about implementing multidimensional databases using OLAP.
Below video has a good introduction about this interesting concept!
Below video has a good introduction about this interesting concept!
Get data type of a table in database dynamically
You can get the data types of columns in a given table daynamically using system tables as given below: Assume 'CurrentStatus' is the table name.
The column name and the data type will be diplayed as result.
The column name and the data type will be diplayed as result.
Tuesday, February 14, 2012
How to find a particular text in the database?
Ex: If you want to find all the places where a particular function is used,
More info on sys_comments
More info on sys_comments
Monday, February 13, 2012
JOIN vs IN vs EXISTS in sql
Difference between IN and EXISTS
- IN will ignore null values where as EXISTS will considers null values as the result.
- JOIN also, will consider null values.
- IN does not consider duplicate values where as JOIN consider duplicates. (To avoid duplicate values, use DISTINCT)
- EXISTS also does not consider duplicate values.
Wednesday, February 8, 2012
Why/ Why not use "WITH RECOMPILE" option?
Once the sproc does not have any syntax errors, it will create entries in sysobjects, sysdepends and syscomments tables. But, it will not compile the query until you execute that.
At the time you execute the proc, SQL Server will create an execution plan and save that in procedure cache for future use.
When the proc executes again, it will re-use the same execution plan, unless otherwise statistics are being changed.
So, if you want to use a new execution plan for each individual execution, use WITH RECOMPILE option in your proc.
Why?
- Optimal use of indexes on columns in a case by case scenario
Why not?
- Improves performance
At the time you execute the proc, SQL Server will create an execution plan and save that in procedure cache for future use.
When the proc executes again, it will re-use the same execution plan, unless otherwise statistics are being changed.
So, if you want to use a new execution plan for each individual execution, use WITH RECOMPILE option in your proc.
Why?
- Optimal use of indexes on columns in a case by case scenario
Why not?
- Improves performance
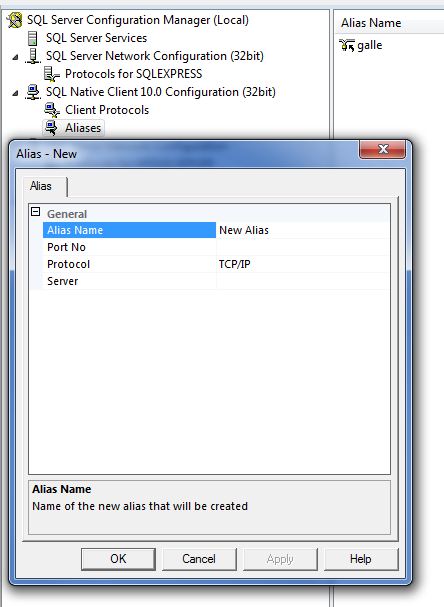
Add an alias to connect database server using SSMS in MSSQL
- All Programs > SQL Server Configuration Manager
- Expand SQL Native Client 10.0 Configuration
- Aliases
- New Alias
Wednesday, October 19, 2011
Why you should not create indexes unnecessary?
Even though indexes improve performance in retrieval, they compromise the performance of inserts and updates.
Why adding a column is more costly than adding a record?
When you are adding a column, a schema lock is placed on the table, so that any connections to the table cannot be made during that time. So, if you can't afford any down time in your system [Always ON], this will definitely be a disadvantage.
Why we should not normalize data?
Since normalization has some well known advantages such as improved indexing, compact databases with less additional records and update performance improvement, I thought of writing about the disadvantages of normalization.
- More Joins - The more joins you use, it will cause more locks to the database, so we should avoid multiple joins when ever possible.
- Performance degrade in data retrieval (SELECT)
Because of that in data warehousing which is used for reporting and analysing, we normally use un-normalized form of data as number of retrievals are greater than inserts and updates.
- More Joins - The more joins you use, it will cause more locks to the database, so we should avoid multiple joins when ever possible.
- Performance degrade in data retrieval (SELECT)
Because of that in data warehousing which is used for reporting and analysing, we normally use un-normalized form of data as number of retrievals are greater than inserts and updates.
Thursday, October 6, 2011
Advantage of having .mdf and .ldf files in two different disks
In SQL Server you can specify the path to database file (.mdf) and log file(.ldf).
When it comes to a server with high no. of transactions and full recovery mode, it is beneficial to have these two paths in two different disks.
Then it will reduce Avg. Disk Queue Length, which is the average number of both read and write requests that were queued for the selected disk during the sample interval, thus resulting a significant improvement in terms of performance.
When it comes to a server with high no. of transactions and full recovery mode, it is beneficial to have these two paths in two different disks.
Then it will reduce Avg. Disk Queue Length, which is the average number of both read and write requests that were queued for the selected disk during the sample interval, thus resulting a significant improvement in terms of performance.
Simple facts about TempDB
- When you create a temp table using # prefix that table will be created in TempDB.
- TempDB is newly created when ever SQL Server is restarted.
- Certain oprations cannot be performed on TempDB such as backup and restore, changing collation, changing schama name, drop the database etc.
SQL Server named instances: Why? Why not?
SQL Server can have one server instance per computer which is the default instance as well as multiple named instances with isolated databases and connections in the same server from SQL Server 2000 onwards. You can access named instances by server name\instance name (Ex: Galle\I01)
Why we need to have multiple named instances other than having one default instances per machine?
So the drawbacks of this approach are performance issues, difficulty to write cross database queries, using different ports for each instance , resource contention on memory and CPU.
Why we need to have multiple named instances other than having one default instances per machine?
- Maximum hardware utilization: Ex: If SQL your server version is designed to use only maximum 2GB RAM and your hardware supports 4GB RAM, you can optimize RAM usage by having two instances in the same server.
- Isolation of databases which have no dependency over each other.
- Better security seperation
So the drawbacks of this approach are performance issues, difficulty to write cross database queries, using different ports for each instance , resource contention on memory and CPU.
Tuesday, September 20, 2011
Join Hints in SQL: Invade the query optimizer!
You can use join hints to tell the query optimizer how you want join operation to be performed. Depending on your preference, it will come up with an execution plan.
There are four types of join hints, namely LOOP, HASH, MERGE and REMOTE.
You may need to decide which join hint would optimize your query based on the type and size of data you are processing.
How ever, it is advisible not to use this feature frequently, unless you have a significant performance improvement, as SQL Server tries it's best to use the best possible join hint by default, mostly it is LOOP.
I have given some execution plans related to different Join hint types below:
There are four types of join hints, namely LOOP, HASH, MERGE and REMOTE.
You may need to decide which join hint would optimize your query based on the type and size of data you are processing.
How ever, it is advisible not to use this feature frequently, unless you have a significant performance improvement, as SQL Server tries it's best to use the best possible join hint by default, mostly it is LOOP.
I have given some execution plans related to different Join hint types below:
Thursday, September 8, 2011
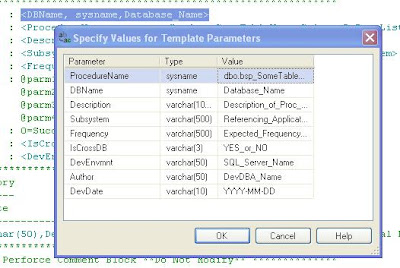
Template parameters in SSMS 2008
You can add templates to varios features in SQL such as stored procedures, tables etc.
Ex:
If you want to replace the values which actual values,
Ex:
If you want to replace the values which actual values,
Tuesday, September 6, 2011
How to change the compatibility level of a database
If any feature is not supported in your current database compatibility level, you will get a syntax error saying you can change it in SSMS.
- In SSMS 2008, go to the database in object explorer under Databases folder.
- Right click the database you want to change the compatibility level.
- In Properties, Options select the option you want in Compatibility level drop down.
Sunday, September 4, 2011
Difference between UNION and UNION ALL
Both UNION and UNION ALL statements can be used in SELECT clause to retrieve a set of records which is in a given column in both tables.
For example, consider the following example:
Here, you can see that there are two tables with a column which is of same data type, StudentName and EmployeeName.
Say we want to find out both the students and employees in this organization, we can use UNION clause and it will return a distinct set of student and employees. If a person is a student as well as an employee, his/her name will appear only once.
But if you use UNION ALL, that person's name will appear twice.
See the results below:
For example, consider the following example:
Here, you can see that there are two tables with a column which is of same data type, StudentName and EmployeeName.
Say we want to find out both the students and employees in this organization, we can use UNION clause and it will return a distinct set of student and employees. If a person is a student as well as an employee, his/her name will appear only once.
But if you use UNION ALL, that person's name will appear twice.
See the results below:
Thursday, September 1, 2011
Difference between COUNT and COUNT_BIG
COUNT will return an int value where as COUNT_BIG will return a big int value.
Difference between COUNT(*) and COUNT(1)
COUNT (*) will return rows related to all the columns with null values. COUNT(1) will return the row count of the first column without null values.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)